Project Member
Derege Tsegaye Meshesha
Assistant Professor at college of Agriculture and Environmental Science Bahir Dar University

Contact Information
Research Theme
- Spatial modeling of soil erosion, land degradation and ecosystem change.
- Studying kinetic energy and erosivity of rainfall.
- Extensive application of remote sensing and GIS technology in natural resource and disaster management
Research key-words
Soil erosion; sediment yield; rainfall kinetic energy; GIS and remote sensing
Research summary
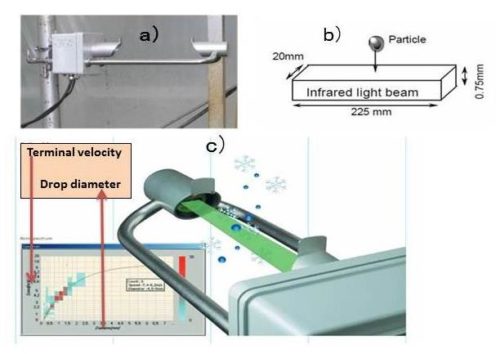
Soil erosion is a natural landscape process that has tremendous impacts on the environment and agricultural productivity. Land use change is recognized as a one of the main triggering factors of erosion. We made investigation on central rift valley (CRV) related to land use change, soil erosion and sediment yield from 1973-2006. Our trend and modeling analysis showed remarkable decrease of vegetation cover and an increase of soil erosion and land degradation. On the other hand, Erosivity, which represents the ability of rainfall to detach soil particles, is an important parameter for quantifying erosion processes. In line with this, we characterized rainfall, and evaluated drop size distribution and kinetic energy of CRV and Northwestern highland of Ethiopia. The findings showed that the raindrop sizes and the kinetic energy of the Ethiopian rain is higher than most of reported in other countries. Moreover, in a controlled situation, we made investigation on kinetic energy and erosivity of simulated rainfall. We found that in all observed intensities, the corresponding kinetic energy of simulated rainfall were higher than the natural rainfall. However, despite the urgent need to improve the estimation of rainfall-caused soil erosion, there has been insufficient works related to rainfall kinetic energy; hence, it remains to be hot research topic for scholars.
Research publication
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., 2012. Continuing land degradation: Cause-Effect in Ethiopia’s central rift valley. Land degradation and development 23: 130-143
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., Haregeweyn, N., 2011. Spatial analysis and semi-quantitative modeling of specific sediment yield in six catchments of the central rift valley of Ethiopia. International Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment 9 (3&4):784-792.
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., Haregeweyn, N., 2012. Analysis of the dynamics and hotspots of soil erosion and its management scenarios: the Case of the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. International journal of sediment Research 27: 84-99.
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., Haregeweyn, N., 2013. Land-use change and its socio-environmental impact in Eastern Ethiopia’s Highland. Regional and Environmental Change 14 (2): 757-768.
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., Haregeweyn, N., Adgo, E., 201 Drop Size Distribution and Kinetic Energy Load of Rainfall Events in the Highlands of the Central Rift Valley, Ethiopia. Hydrological Science Journal 59 (12): 2203-2215.
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., Haregeweyn, N., Adgo, E., 201 Evaluating Spatial and Temporal Variations of Rainfall Erosivity, Case of Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Theoretical and Applied Climatology. DOI: 10.1007/s 00704-014-1130-2.
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Haregeweyn, N., Determination of soil Erodibility using fluid energy method and measurement of the eroded mass. Geoderma 284:13-21.
- Meshesha, D.T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., Haregeweyn, N., Tegegne, F., Evaluation of kinetic energy and erosivity potential of simulated rainfall using Laser Precipitation Monitor. Catena 137:237-243.